Project Management Methodologies
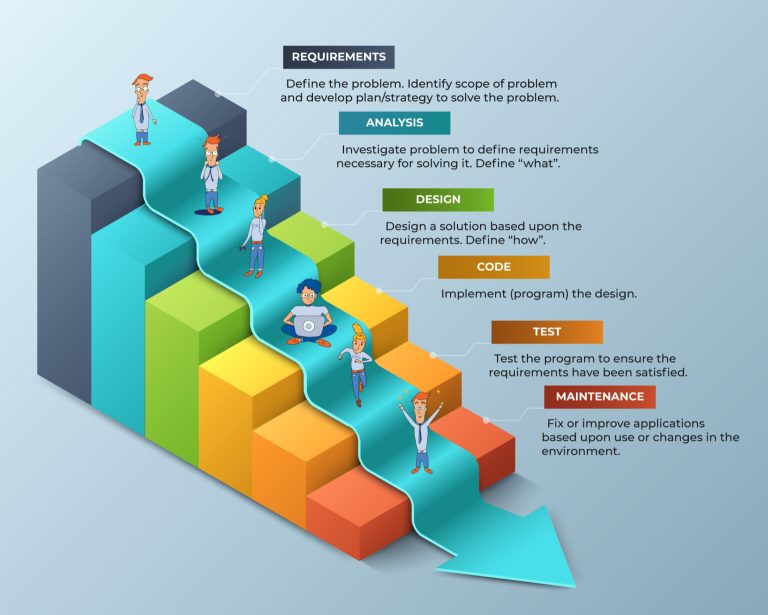
Waterfall Methodology
This is the most widely used project management methodology, particularly prevalent in construction projects.
Common ranges for Execution Delivery % in Waterfall projects:
- 0-20%: Low progress, project is behind schedule
- 20-50%: Moderate progress, project is on track but with some delays
- 50-80%: Good progress, project is on track and meeting deadlines
- 80-100%: High progress, project is ahead of schedule
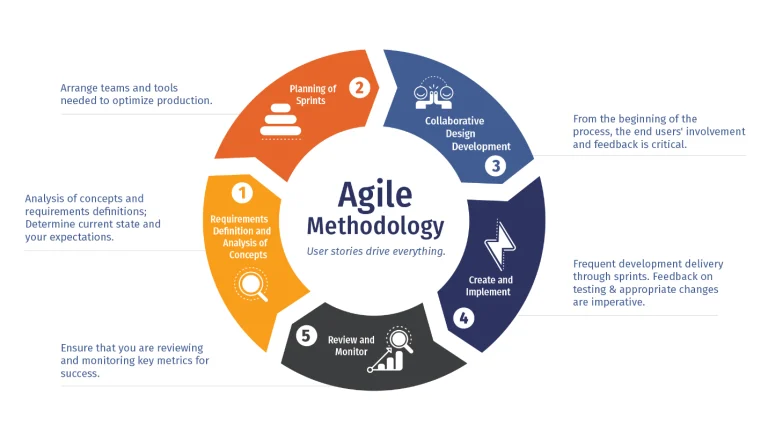
Agile Methodology
is an excellent approach for projects that are centered around partial deliverables, especially when these deliverables can be measured independently and have minimal dependencies on each other, allowing for iterative testing.
Community benchmarks suggest that, for Agile teams, a completion rate for delivered items in a sprint typically ranges from 70% to 90% and maintaining a consistent velocity is often more critical than achieving a specific percentage.

(1)Project Ideation- Initiation
are crucial stages in project management that lay the groundwork for successful execution. The process includes several key steps:-
- Idea Evaluation and Selection: Evaluate idea
- Define Project Vision and Goals
- Define Project Scope:
- Develop Preliminary Budget and Timeline
- Create a Project Charter /Formulate Team
- Prepare for Project Kick-off
(2) Project Planning
is a critical phase in project management that involves outlining the scope, objectives, tasks, resources, timelines, and potential risks associated with a project.
- Define Goals and Objectives:
- Identify Stakeholders:
- Develop Project Scope: Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to clarify project inclusions.
- Create a Timeline: Utilize Gantt charts or software to visualize
- Resource Planning.
- Budgeting.
- Communication Plan.
- Risk Management.
- Implementation Plan
(3)Project Execution
is a crucial phase in project management focused on implementing planned activities to achieve objectives. It encompasses several key elements:
- Team Coordination: Clarifying roles for effective collaboration.
- Task Implementation: Carrying out tasks per the project plan while meeting timelines and quality standards.
- Resource Management: Efficiently managing personnel, materials, and finances.
- Communication: Keeping stakeholders updated and addressing any issues.
- Monitoring Progress: Assessing performance against the plan to ensure adherence to schedule and budget.
- Risk Management: Identifying and addressing potential risks proactively.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring deliverables meet required standards.
Effective project execution demands adaptability, strong problem-solving skills, and ongoing monitoring to maintain project alignment.
(4)Project Monitoring Control
crucial for keeping projects on track regarding scope, timeline, and budget. It involves systematic performance tracking using key components, including:
- Performance Measurement: Utilizing KPIs and metrics such as schedule variance (SV) and cost performance index (CPI) to assess project performance.
- Progress Tracking: Employing tools like Gantt charts to monitor task completion and timelines.
- Issue and Risk Management: Actively identifying and resolving challenges to reduce their impact.
- Change Control: Managing project changes through a structured process to ensure all alterations are documented and approved.
- Reporting: Regularly updating stakeholders on project status and challenges.
- Evaluation and Adjustment: Continuously reviewing and refining project processes to align with objectives.
(5)Project Closing
The final phase of project management, ensuring the project meets its objectives and is formally concluded. Key components include:
- Final Deliverables: Verification that all deliverables are completed and meet standards.
- Documentation: Compilation of all project-related documents for future reference.
- Stakeholder Approval: Gathering feedback and approval from stakeholders.
- Financial Closure: Finalizing all financial matters, including settling invoices.
- Lessons Learned: Conducting a review to identify successes and areas for improvement.
- Team Acknowledgment: Celebrating team contributions and formally releasing team members.
- Archive Information: Storing relevant project documentation for future use.
This phase ensures successful completion and allows the project team and stakeholders to move forward effectively.
Projects Variations and Claims Roadmap
The Project Claim Management Process Roadmap by TAYCOON-UK is a step-by-step guide for managing claims during a project.
The process includes 8 steps:-[ identifying potential claims, analyzing and assessing the claim, investigating ,reviewing and analyzing, monitoring and controlling, resolving disputes, and negotiating, resolving and closing and documenting lessons learned.]
The roadmap provides a structured approach to managing claims and ensures that all stakeholders are informed and aligned throughout the process.

